Tools
Introduction
A tool is an uninstantiated class that implements at least the BaseTool interface.
Tools can be configured via their constructor. To use a tool, one must:
- Add the uninstantiated tool using the library's top level
addToolfunction - Add that same tool, by name, to a ToolGroup
Here we will introduce several concepts about tools (annotation and segmentation tools)
inside Cornerstone3DTools.
Tools
Manipulation Tools
Cornerstone3DTools provides a set of tools that can be used to manipulate the
images in the viewports. These include:
- enabling zooming in and out of the image (
ZoomTool) - performing panning and navigation of the image (
PanTool) - scrolling through the image (
StackScrollMouseWheelTool) - manipulating the windowLevel of the image (
WindowLevelTool)
Annotation Tools
Cornerstone3DTools provide a set of annotation tools. You can use these tools
to create and edit annotations for use cases such as:
- Measuring distance between two points (Length Tool)
- Measuring height between two points (Height Tool)
- Measuring width and length for a structure (Bidirectional Tool)
- Measuring area and statistics for a rectangular area (RectangleRoi Tool)
- Measuring volume and statistics for a ellipsoid (EllipseRoi Tool)
- Getting the underlying value for a voxel (Probe Tool)
Below, you can see a screenshot of the annotation tools that are available in Cornerstone3DTools.
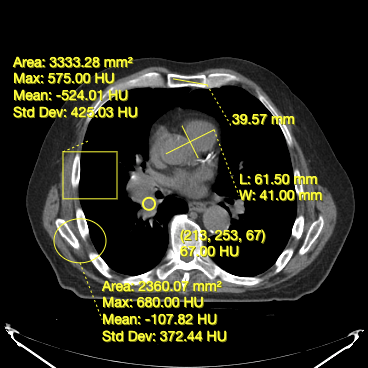
Dynamic tool statistics
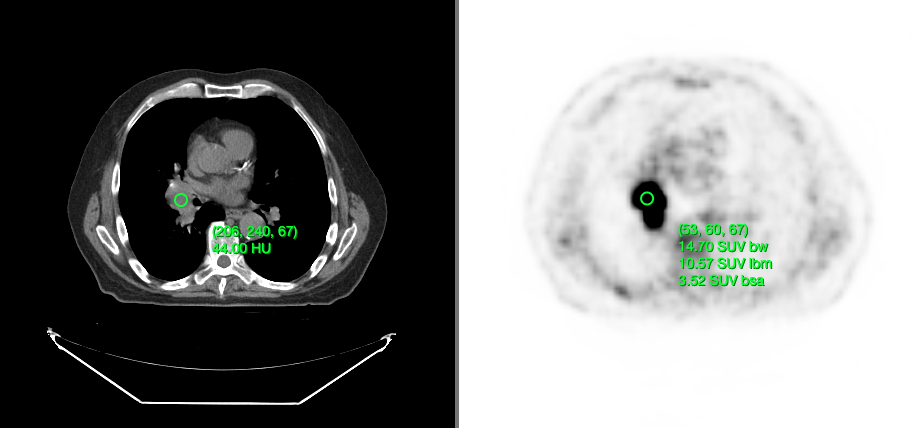
Cornerstone3DTools is capable of calculating dynamic statistics based on the modality of the volume being rendered. For instance, for CT volumes a ProbeTool will give Hounsfield Units and for PET it will calculate SUV stats.
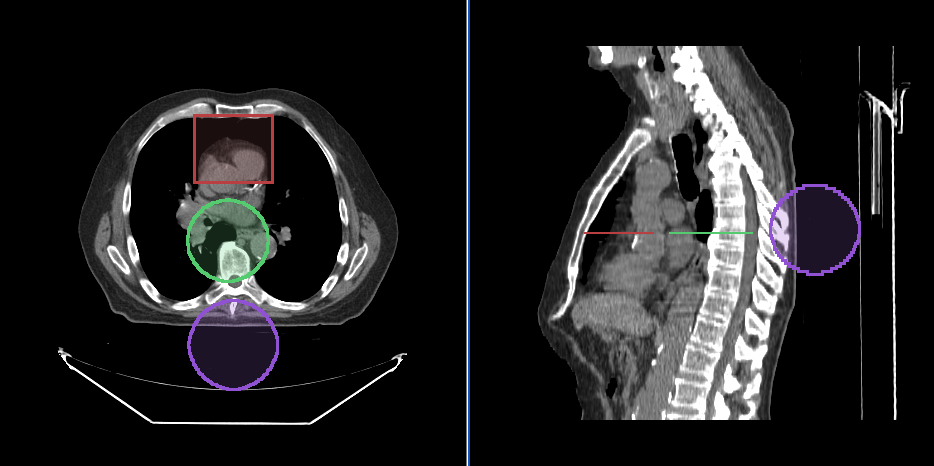
Annotation sharing in Frame of Reference
Since, annotations are stored in the patient physical space, if there are two viewports that are displaying the same frame of reference, they will share the same annotations.
Segmentation Tools
Cornerstone3D also provides segmentation tools. This includes3D segmentation editing tools such as brush, rectangle and circle scissors, and
3d sphere tools.
We will discuss in length the different types of segmentation tools and how they
are used in Cornerstone3DTools in Segmentation section.
How tools work internally
mouse and keyboard fire events, these events are captured and normalized by
Cornerstone3DTools. The normalized events are then fired and handled by
tools either as mouseDown, mouseDrag and mouseUp events.
Adding Tools
The Cornerstone3DTools library comes packaged with several common tools. All implement either
the BaseTool or AnnotationTool. In order to be able to use the tools, you must
first add them to the Cornerstone3DTools. You can do this by using the addTool function.
import * as csTools3d from '@cornerstonejs/tools';
const { PanTool, ProbeTool, ZoomTool, LengthTool } = csTools3d;
csTools3d.addTool(PanTool);
csTools3d.addTool(ZoomTool);
csTools3d.addTool(LengthTool);
csTools3d.addTool(ProbeTool);
Adding a tool to the library will only let the library know about the tool. It will not automatically add the tool to any tool groups, nor will it instantiate the tool for usage.
Tool Modes
Tools (in their toolGroup) can be in one of four modes. Each mode impacts how the tool responds to interactions.
There should never be two active tools with the same binding
| Tool Mode | Description |
| Active |
|
| Passive (default) |
|
| Enabled |
|
| Disabled |
|